Nội dung bài viết
Potassium hydroxide is a highly corrosive industrial chemical, commonly used in many fields, especially in the fertilizer and cosmetics industries. So what is potassium hydroxide, its typical physicochemical properties and important practical applications? The article below Trường Chu Văn An will help you answer all your questions about this compound!
1. Physical properties of Potassium hydroxide KOH
|
Physical state |
Solids |
|
Color |
White |
|
Smell |
Odorless |
|
Boiling temperature |
1.327oC (1.6000 K; 2.421 oF) |
|
Melting temperature |
406 oC (679 K; 763 oF) |
|
Water solubility |
97 g/ml (0 oC) 121 g/ml (25 oC) 178 g/ml (100 oC) |
|
Ability to dissolve other substances |
Soluble in alcohol, glycerol Insoluble in ether, liquid ammonia |
|
Specific volume |
2.044 g/cm3 |
|
pH |
13 |
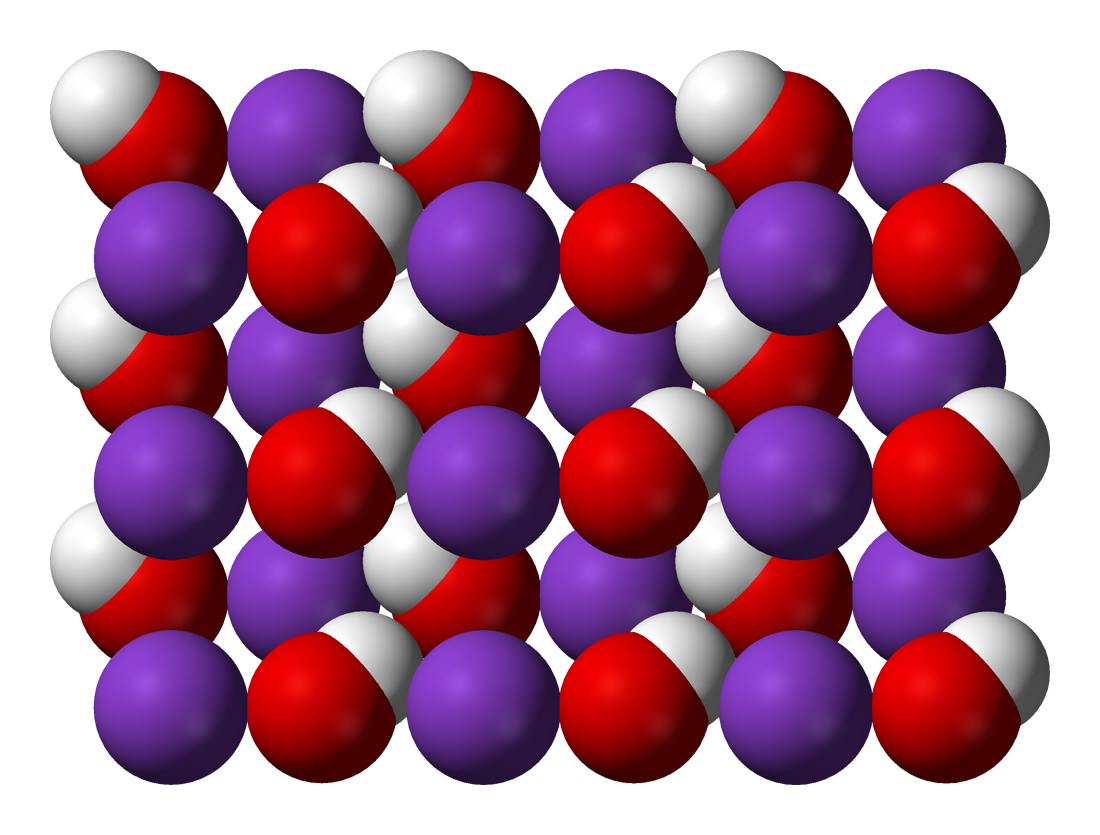
Molecular structure of Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is a strong base, easily reacting with water and carbon dioxide in the air to form potassium carbonate.
In solution form, it has the ability to corrode glass, fabric, paper, and leather, and in molten solid form, it can corrode porcelain and platinum.
2. Chemical properties of KOH
- It is a strong base capable of changing the color of indicators such as turning red litmus to blue and colorless phenolphthalein solution to pink.
- At room temperature, KOH reacts with acid oxides such as SO2 and CO2
KOH + SO2 → K2SO3 + H2O
KOH + SO2 → KHSO3
- Reacts with acids to form salt and water
KOH(dd) + HCl(dd) → KCl(dd) + H2O
- Reacts with organic acids to form salts and hydrolyze esters and peptides
RCOOR1 + KOH → RCOOK + R1OH
- Reacts with strong metals to form new bases and new metals
KOH + Na → NaOH + K
- React with salt to form new salt and new acid
2KOH + CuCl2 → 2KCl + Cu(OH)2↓
- KOH is a strong base, in water it completely dissociates into Na+ and OH- ions.
- Reacts with some metal oxides whose oxides and hydroxides are amphoteric such as aluminum, zinc,…
2KOH + 2Al + 2H2O → 2KAlO2 + 3H2↑
2KOH + Zn → K2ZnO2 + H2↑
- Reacts with some amphoteric compounds
KOH + Al(OH)3 → KAlO2 + 2H2O
2KOH + Al2O3 → 2KAlO2 + H2O
- Some other common reaction equations of Potassium hydroxide
2KOH + 2NaHCO3 → K2CO3 + Na2CO3 + 2H2O
2KOH + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2H2O
3Cl2 + 6KOH 5KCl + KClO3 + 3H2O
P2O5+ 6KOH → 2K3PO4 + 3H2O
KOH + CH3COOH → CH3COOK + H2O
3KOH + H3PO4 → K3PO4 + 3H2O
3Br2 + 6KOH → KBrO3 + 5KBr + 3H2O
KOH + HNO3 → KNO3 + H2O
CO2 + KOH → KHCO3
>> Product reference: Potassium Hydroxide KOH 90% Korea
3. Industrial production methods of potassium hydroxide
3.1. Electrolysis of potassium chloride solution
Potassium chloride is carried away for electrolysis in an electrolysis tank with a membrane with an inert anode catalyst at a temperature of 75 oC.
2H2O + 2KCl → 2KOH + H2 + Cl2
However, this method is not economically effective because the cost of potassium chloride is quite high. At the same time, the amount of electricity needed for electrolysis is not small. In particular, the potassium chloride solution you want to use needs to go through a purification process to lower the heavy metal content to the ppb level before it can be put into the electrolysis tank to protect the diaphragm, and KOH is created accordingly. There is also a purity guarantee. The cost for the whole process is quite large while commercial potassium hydroxide does not need such high purity.
3.2. Production of Potassium hydroxide from Potassium formate
Because of the shortcomings of the method of electrolysis of potassium chloride solution with a membrane, people have turned to another, much more effective method, which is using potassium formate.
Potassium format production process:
Using technology from SRI Consulting company
- Convert natural gas mixture into CO and H2 by steam reforming process.
CH4 + H2O → CO + 3H2
- Passing CO gas through slaked lime solution Ca(OH)2 forms calcium formate Ca(HCOO)2.
Ca(OH)2 + 2(CO + 3H2) → Ca(HCOO)2 + 6H2
- Use solvent extraction or ion exchange method to convert Calcium formate into Potassium formate KCOOH.
+ Extraction method: Calcium formate solution will react with solid potassium chloride in an extraction device with an organic solvent containing CO group such as butanol or pentanol. K and Ca exchange reactions will occur locally.
Ca(HCOO)2 + 2KCl → 2KCOOH + CaCl2
+ Ion exchange: Calcium formate solution is added to the ion exchange device with available potassium. Then, K+ ions enter the water phase to create potassium formate solution, Ca+ ions will be absorbed by the cation exchange device. Continue using Potassium chloride, Potassium is absorbed by the exchanger and the water phase will be a CaCl2 solution that can be removed.
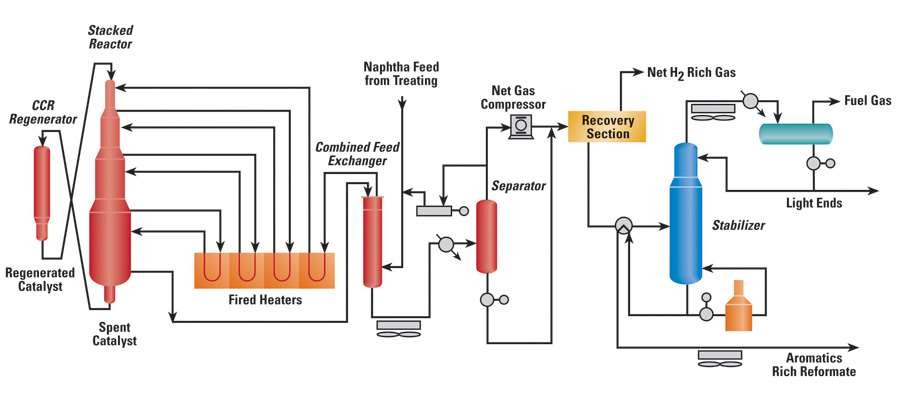
Steam reforming process
Potassium hydroxide KOH production process:
Method 1: You can use furnaces, Thelen equipment or modern solution oxidation systems to calcine Potassium formate with pre-prepared KOH.
2KCOOH + 2KOH + O2 → 2K2CO3 + 2H2O
2K2CO3 + 2Ca(OH)2 → 4KOH + 2CaCO3
- If you only want to produce KOH
2KCOOH + 2Ca(OH)2 + O2 → 2KOH + 2CaCO3+ 2H2O
- If you only want to produce Potassium carbonate K2CO3
2KCOOH + Ca(OH)2 + O2 → K2CO3 + CaCO3+ H2O
Method 2: Metabolized to Potassium oxalate K2C2O4
- Heating potassium formate at a temperature of 300-350 oC with KOH catalyst, circulating potassium oxalate and nitrogen gas.
- Conducts potassium oxalate through slaked lime solution to form KOH.
4. In life, what is potassium hydroxide used for?
- KOH is used to adjust the pH in highly acidic chemical fertilizers such as KH2PO4 before being used to fertilize crop varieties sensitive to pH fluctuations.
- Potassium hydroxide is used to perform extraction processes where sodium hydroxide cannot be used or can be used but is ineffective, such as extracting dolomite ore to obtain alumina.
- Compared to sodium hydroxide, the use of potassium hydroxide will be more effective in the production of detergents such as soap, shampoo,… barn cleaning agents, and industrial detergents.

Hand soap
- Potassium hydroxide is used to treat light ash to produce Potassium aluminate and Potassium silicate. Continuing to hydrolyze potassium aluminate will yield potassium hydroxide and aluminate for reuse.
- Use KOH to prepare Vinyl bromide, Ethylene bromide:
C2H4Br2 + KOH → CH2Br + KBr + H2O
- KOH is used to produce many potassium salts by reaction with acid oxides or acids such as permanganate, phosphate, potassium carbonate, cyanide and silicates.
KOH + SO2 → K2SO3 (Potassium phosphate) + H2O
KOH + CO2 → K2CO3 (Potassium carbonate) + H2O
KMnO4 + K2SO3 + KOH → K2MnO4(Potassium permanganate) + K2SO4 +3 H2O
- Production of biodiesel by converting triglycerides in vegetable oil. Using potassium hydroxide to treat diesel oil creates Glycerin – a low-cost animal feed (after removing methanol).
- People use KOH to produce alkaline batteries.

Manufacturing batteries
- Potassium hydroxide participates in the oil and gas refining process with the role of removing organic acids and sulfur-containing compounds.
- In medicine, KOH compounds are used to diagnose fungal diseases and treat warts.
- In leather production, people soak the skin in KOH solution to help remove hair from the skin layer.
- Using KOH solution with a concentration of 3-5% will help identify some types of fungi such as boletes, polypores, gills, and lichens.
- Potassium hydroxide is used in the metallurgical industry to remove rust, treat metal surfaces, and alloys that are not affected by the corrosive properties of KOH.

Removes rust from metal surfaces
- Producing dyes, nail polish removers,…
5. Dangerous properties of Potassium hydroxide
- Potassium hydroxide is caustic and very dangerous. They have strong oxidizing properties that can mutate stem cells, causing acute or chronic toxicity to the aquatic environment.
- Skin contact: Causes skin allergies, blistering, can cause burns and scarring.
- Eye contact: Damages the mucous membrane, causing pain, swelling, and red eyes. More dangerous than blindness.
- Respiratory exposure: If inhaled in small amounts and low concentrations, it will cause mild allergies, sneezing, runny nose, and sore throat. If the inhalation time is long and the Potassium hydroxide vapor has a high concentration, the victim may develop pneumonia.
- Contact with the digestive tract: Swallowing KOH will cause burns in the throat, mouth, and stomach. If not treated promptly, leaving the victim poisoned for more than 5 hours will lead to death.

Danger warning
5.1. Medical first aid measures for potassium hydroxide infection
- Skin contact: Immediately remove exposed clothing. If you want to use it next time, wash it thoroughly. For skin areas affected by KOH, wash thoroughly with water and use soap if available before contacting a doctor.
- Eye contact: Immediately flush eyes with clean water for at least 15 minutes, combined with continuous eye rotation. Take the victim to the nearest medical facility for further examination and treatment.
- Respiratory contact: Move victim to a cool area. If the victim stops breathing, perform artificial respiration and then immediately transfer to the nearest medical facility for treatment.
- Contact with potassium hydroxide through the digestive tract: Do not induce vomiting or give the victim anything to eat or drink. If the victim vomits, keep the head higher than the waist to prevent the victim from breathing in toxic fumes. Take the victim to the nearest medical facility.
5.2. Measures to handle problems caused by potassium hydroxide leaks
- If the amount of chemical leakage is small, you can use soil or vermiculite to cover it, collect it in a container and destroy it. Use dilute acid such as acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, etc. to neutralize the remaining KOH.
- If the amount of KOH leak is large, it is necessary to isolate the dangerous area, prevent it from spreading to the water system, sewer lines, etc. and try to capture as much chemical as possible into the container and then treat the remaining portion. residual as with a small amount of leakage.
5.3. Safety notes with Potassium hydroxide
Preserve:
- The storage area must be airy, dry, and have a good ventilation system. Minimize items that can catch fire.
- Containers and sacks must be sealed.
- Avoid mixing potassium hydroxide with incompatible substances such as aluminum and magnesium.
Use:
- When dissolving potassium hydroxide with water, only add it to the water and not the other way around.
- Equipped with labor protection equipment according to NIOSH standards. Note that air filtering gas masks will not be effective in areas lacking oxygen.

Storage of potassium hydroxide
6. Trường Chu Văn An – Distributor address for quality Potassium hydroxide, good price
If you are looking reputable chemical distributor Trường Chu Văn An is the number 1 priority choice today. With 20 years of experience in the field of importing and supplying laboratory chemicals and industrial chemicals, we always attach importance to developing the company’s standard culture with core values: Considerate – Friendly. – Professionalism – Prestige – Responsibility.
Trường Chu Văn An’s chemical products all meet ISO 9001:2015 quality management standards and ISO 14001:2015 environmental management standards and are strictly tested by a team of highly qualified supervisory staff. from the import process to packaging and distribution of products.

Trường Chu Văn An- Prestigious address for purchasing industrial chemicals
If you have any questions about Potassium hydroxide products, please contact hotline 0826 010 010 for advice and the best price quote.
7. Frequently asked questions
What is the pH of KOH?
The pH value of 0.001M KOH solution is 11
Is KOH an electrolyte?
KOH is a strong electrolyte
Why does NaCl not react with KOH?
NaCl is a neutral salt, KOH is a base so it cannot react in a neutralization reaction. If the exchange method is not satisfied, it creates a precipitate, evaporates or weak electrolyte. Therefore the reaction does not occur.
What color does KOH turn red litmus?
KOH turns red litmus to blue
Does KOH precipitate?
KOH is a strong alkali and when dissolved in water it forms a strong alkaline solution. KOH solution does not form a precipitate because all its particles are completely soluble in water.
What is the atomic mass of KOH?
The atomic mass of KOH is about 56.1 g/mol.
See more:
- Answers about the basic characteristics and applications of Potassium
- Overview of Sodium – Properties and practical applications


Nội dung được phát triển bởi đội ngũ truongchuvananhue.edu.vn với mục đích chia sẻ và tăng trải nghiệm khách hàng. Mọi ý kiến đóng góp xin vui lòng liên hệ tổng đài chăm sóc: 1900 0000 hoặc email: hotro@truongchuvananhue.edu.vn