Nội dung bài viết
Medium voltage electrical cabinets play an important role in distributing, controlling and monitoring medium voltage electrical systems. However, due to operating at high voltage levels, medium voltage electrical cabinets are potentially dangerous when not operated properly. In this article, we will learn with you what a medium voltage electrical cabinet is, as well as its structure, classification and notes when installing medium voltage electrical cabinets.
What is a medium voltage electrical cabinet?
According to voltage level standards in Vietnam, medium voltage electrical cabinets operate on medium voltage power networks, with voltage levels from 1 – 35kV. This type of cabinet undertakes 3 main tasks including:
- Distributing and regulating power from high voltage transformer stations to medium voltage loads.
- Switching and protecting medium voltage power lines against electrochemical incidents.
- Ensuring stability and continuity in the national power transmission grid.
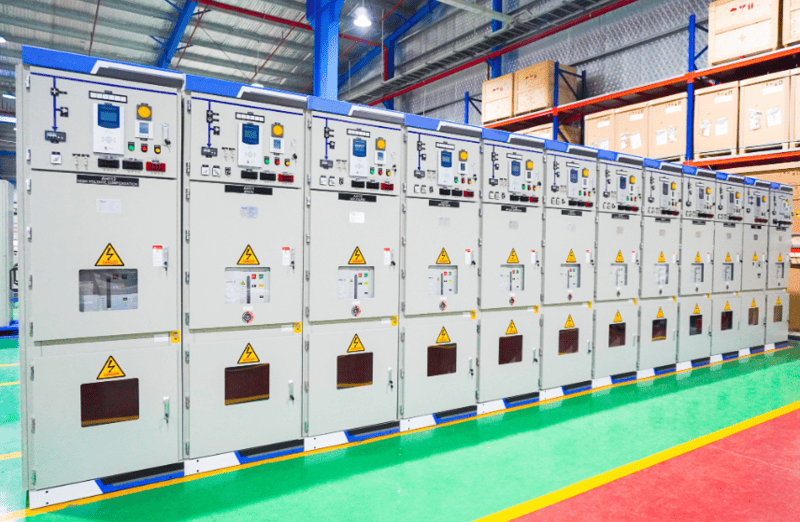

Medium-voltage electrical cabinets are commonly installed at power plants, transformer stations, power distribution stations of Electricity companies, in industrial parks, residential areas or medium-voltage power stations of medium-voltage electricity consumption areas such as airports, hospitals, high-end urban areas, commercial centers…
Structure of medium voltage electrical cabinet
Operating at high voltage levels, medium voltage electrical cabinets must meet strict technical and electrical safety standards in design and production such as IEC 62271 (Standards for voltage equipment), IEC 60947 (Standards for switchgear and medium voltage electrical equipment), TCVN 6360 (General Vietnamese standards for electrical cabinets and medium voltage equipment). Accordingly, electrical cabinets of this type must be made from high-quality materials to meet the ability to protect equipment and internal components, while ensuring safe insulation for operators.
In terms of structure, a typical medium voltage electrical cabinet usually consists of two main components: the cabinet shell and the internal modules.
Electrical cabinet cover
Medium-voltage electrical cabinet shells must be thick corrugated iron, electrostatically painted, galvanized or made from high-quality stainless steel, to ensure resistance to water, moisture, fire, and mechanical impact to protect the complex electrical equipment inside.
The insulation layer adjacent to the cabinet serves to isolate the electrical component and the operator or surrounding environment. In addition, inside the cabinet there is a layer of door called the cabinet’s internal protection door, which is responsible for protecting the switching devices.
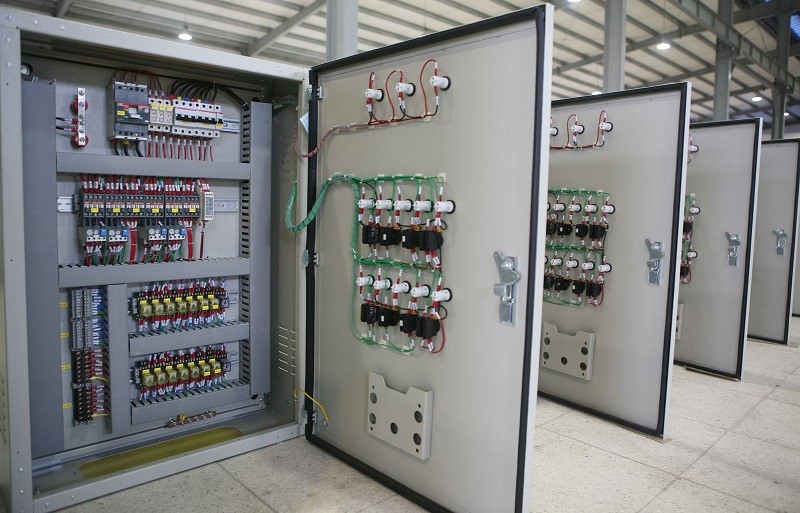

Functional chambers
The main group of equipment in medium voltage electrical cabinets of all types is switching equipment with the ability to quickly turn on and off such as VCB, LBS, DS disconnector or Recloser. Most of these devices will be arranged in modules corresponding to different functions inside the electrical cabinet. The modular design also allows components of the medium voltage electrical cabinet to be replaced/upgraded easily.
- Circuit Breaker Compartment: Designed to withstand high current and voltage, specifically containing the main switching devices of medium voltage electrical cabinets. When an electrical problem occurs, the internal circuit breaker will automatically cut off the circuit to protect the system.
- Switchgear Compartment: Is the place that contains important protection and switching devices such as VCB circuit breakers, DS disconnectors, protective relays, current and voltage sensors.
- Cable Compartment: The part that connects, organizes and routes electrical cables to devices in the cabinet. The cable connection chamber not only helps cables to be neatly and aesthetically arranged, but also has the function of protecting electric cables from vibration, collision, electromagnetic interference and is convenient for repair and maintenance work.
- Low Voltage Compartment: The part that connects the medium voltage electrical cabinet to the low voltage electrical system. This contains the controllers, measuring units and low voltage grounding. The main function of the low voltage chamber is to distribute low voltage to conductors, circuit breakers and isolators, for the purpose of providing main power in the building or auxiliary electrical systems.
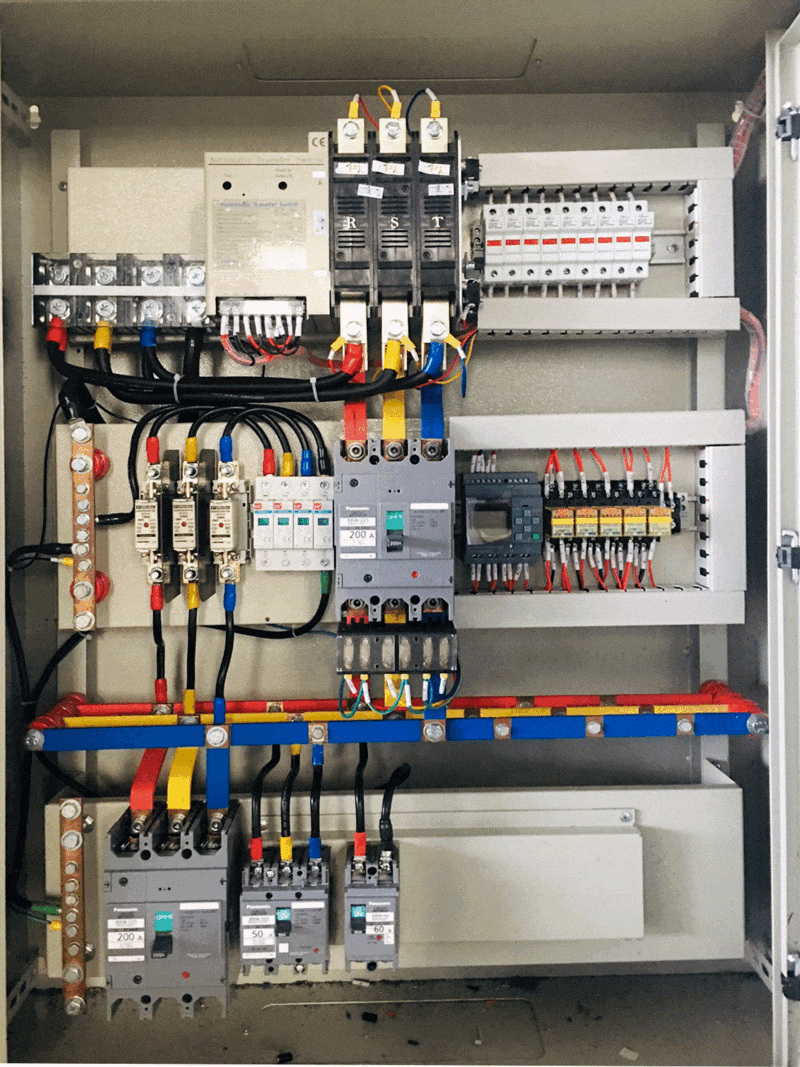
How to classify medium voltage electrical cabinets
There are many criteria to classify medium voltage electrical cabinets. Below are the most common ways to classify electrical cabinets.
According to voltage level
- 1 phase medium voltage cabinet: Used for single-phase medium voltage power systems, with voltage levels from 1 to 22kV, commonly at 6kV, 10kV, 22kV. The main function of this type of cabinet is to distribute electricity from the medium voltage transformer station to individual consumers or small projects.
- 3-phase medium voltage cabinet: The most popular type of medium voltage cabinet, suitable for 3-phase medium voltage grid.
According to grounding type
- Above grounding cabinet: Applicable to cabinets with a grounding system above.
- Grounding cabinet below: Used for grounding cabinet systems below.
By function
- Medium voltage switchgear: Based on the main switching device, medium voltage switchgear is divided into many types such as VCB cabinets – using vacuum insulation technology, LBS cabinets specialized in cases where continuous switching is needed. DS disconnectors are simpler switching devices, used to isolate elements of medium voltage power systems.
- RMU cabinet (Ring Main Unit): This type of cabinet uses a loop power network to provide power to each specific area. The main equipment in the RMU cabinet includes circuit breakers VCB, LBS and controller.
- Medium voltage ATS cabinet: Helps automatically switch power between the two main sources and the backup source, ensuring the system is not interrupted due to power outages.
- Medium voltage capacitor cabinet: Contains a capacitor with the function of compensating reactive power, increasing the cosφ coefficient, improving power quality.
- Second cabinet: Create separate chambers to isolate different equipment and circuits, thereby increasing safety in the electrical system.
According to the type of insulation
- Gas insulated cabinet (GIS): Use SF6 gas as an insulating medium. The switching devices will be placed in a sealed tank filled with SF6 gas and completely isolated from the outside environment. The advantage of gas insulated cabinets is compact size, optimal installation space, but high investment costs and operation and maintenance also require specialized technicians.
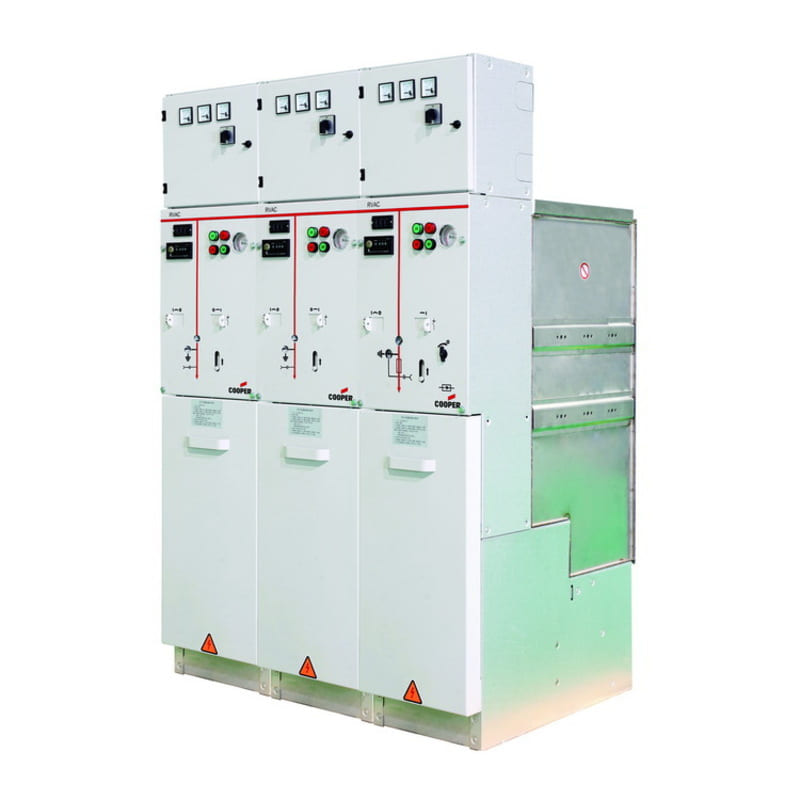

- Air-insulated cabinet (AIS): AIS medium voltage cabinets use air as an insulating medium. The main switching devices are located in open spaces or in closed chambers. This type of insulation helps save investment and operating costs but requires a large installation area, and insulation performance is easily affected by moisture and dust.
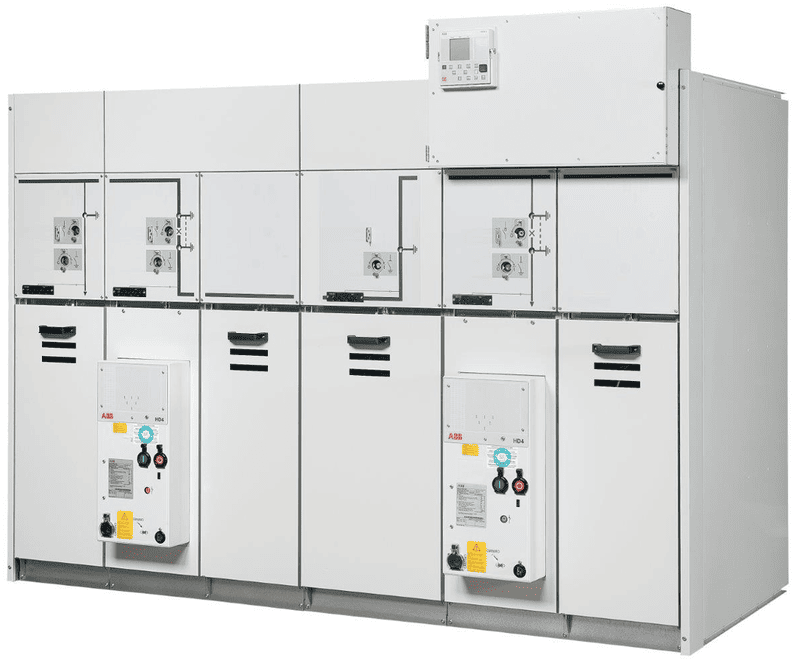
- Solid Insulated Cabinet (SIS): Use solid materials such as epoxy or polyurethane as an insulating medium, completely covering electrical components including circuit breakers, disconnectors, bus bars… This electrical cabinet is suitable for installation in specific harsh environments such as oil fields, chemical plants, providing higher safety and minimizing the risk of gas leaks. However, solid insulation cabinets have an expensive investment cost, so they are not suitable for many systems.
Basic medium voltage electrical cabinet installation process
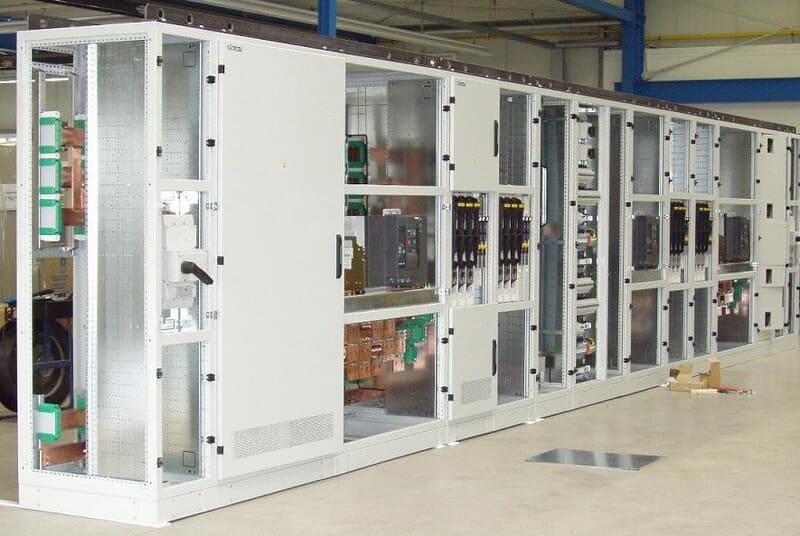

To install a medium voltage electrical cabinet, the operator needs to have highly specialized skills and knowledge. The following is the most basic process of installing medium voltage electrical cabinets.
- Determine installation location: The electrical cabinet should be placed in a dry location, away from moisture sources, heat sources and interference sources from other electrical equipment. In particular, the installation location of medium voltage electrical cabinets needs to be easy to access, without obstacles.
- Choose an electrical cabinet suitable for the intended use: Medium voltage electrical cabinets suitable to the needs and requirements of the electrical system will determine the effectiveness and safety during operation.
- Carefully check the technical specifications: Some important specifications you need to check include rated voltage, rated current, rated power, protection level (IP), controller type, cut-off time and insulation resistance. Make sure these parameters are compatible with the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Connecting and installing equipment: First of all, it is necessary to clearly understand the principle diagram of a medium voltage electrical cabinet to accurately determine the secondary connection drawing and the number and location of important electrical equipment in the cabinet. Then prepare all necessary equipment and components and follow the installation steps specified in the manufacturer’s documents. Finally, test operation after the connection process is completed.
- Set up a monitoring and protection system for electrical cabinets: Ensure a stable and continuous power supply to the medium voltage electrical cabinet, and also need to equip additional warning and protection systems to ensure safety in case an electrical incident occurs. The use of voltage converters and switchgear also helps medium voltage electrical cabinets operate effectively against impacts from the external electrical network.
- Acceptance of the entire system: After installation, it is necessary to test and accept all electrical lines, connections, grounding systems, especially switching and measuring devices, as well as the operation of electrical cabinets when opening and closing the power source. If any errors arise, they should be corrected immediately.
Some notes when installing medium voltage electrical cabinets:
- Before proceeding with installation, the principle diagram of the medium voltage electrical cabinet must be designed absolutely accurately.
- Equipment and auxiliary materials for electrical cabinets such as connectors, timers, dials, etc. must be fully prepared before the installation process.
- Choose a ground wire suitable for the medium voltage electrical cabinet, preferably the soft, flat, mesh type.
- Strictly comply with the manufacturer’s installation instructions and technical regulations.
- Any electrical cabinet needs to be tested and system evaluated before being put into official operation. You can test the electrical system by connecting it in series with a 300W light bulb, then try again with another load.
- Periodically check and maintain electrical cabinets to promptly detect potential problems.
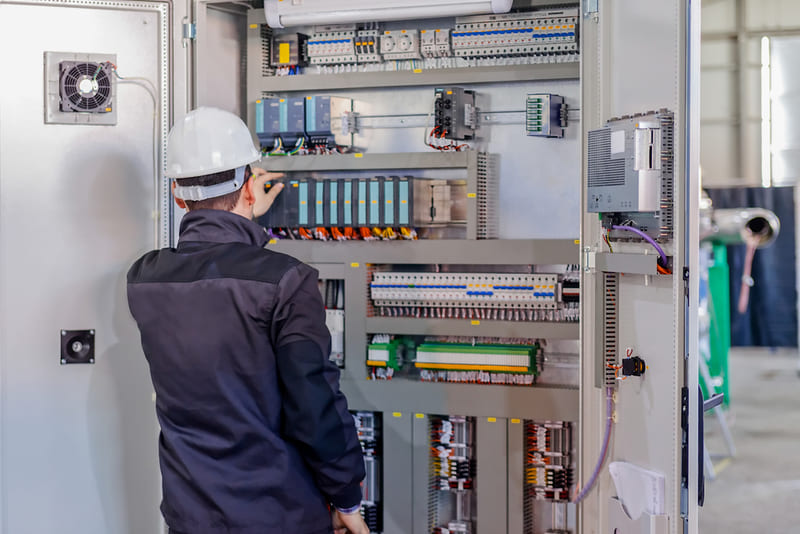

Compare medium voltage electrical cabinets and low voltage electrical cabinets
These are 2 types of cabinets used for 2 different voltage networks. Due to the difference in input voltage, medium voltage electrical cabinets and low voltage electrical cabinets also have different characteristics.
Voltage handling ability
Low voltage electrical cabinets operate at voltage levels below 1kV, while medium voltage electrical cabinets are used in systems with voltage levels from 1 – 35kV. Therefore, medium voltage cabinets are capable of handling higher voltages than low voltage cabinets.
Short circuit tolerance
Medium voltage electrical cabinets are designed to prevent short circuits with many switching tools such as switches, circuit breakers, circuit breakers, transformers… Compared to low voltage electrical cabinets, the short circuit tolerance of medium voltage cabinets is much higher.
Space is reduced
Medium-voltage cabinets have a typical structure consisting of many different equipment chambers, so the space is reduced (or the minimum insulation distance between live equipment or live parts and the cabinet shell) is also more limited than low-voltage cabinets.
Meanwhile, low-voltage cabinets have a quite simple structure, usually only consisting of the cabinet shell and equipment installation panel, so the space is reduced and is flexible, depending on the size and thickness of the cabinet shell.
To better understand the difference between medium voltage electrical cabinets and low voltage electrical cabinets, you can follow the following comparison table:
| Element | Medium voltage electrical cabinet | Low voltage electrical cabinet |
| Operating voltage level | 1kV – 35kV | Below 1kV (popular 220V for civil purposes and 380V for industrial purposes) |
| Structure | Large size, divided into many separate functional chambers | Smaller, simple interior design, can be divided into functional compartments or not |
| Space is reduced | Small | Big |
| Short circuit tolerance | High | Lower |
| Insulating materials | SF6, air, insulating oil | Compressed air, insulating plastic |
| Switching equipment | VCB, LBS, DS, Recloser | ACB, MCCB, MCB,… |
| Main function | Distribute and control power from the substation to medium voltage loads | Distribute and control power from the substation to low voltage loads |
Frequently asked questions about medium voltage electrical cabinets?
Question 1: At what voltage level do medium voltage electrical cabinets in Vietnam operate?
Reply: According to EVN regulations, medium voltage electrical cabinets operate at voltages from 1 – 35kV.
Question 2: Why do medium voltage electrical cabinets require strict design, construction and installation standards?
Reply: Operating at high voltage levels, the risk of electrical accidents in medium voltage cabinets is very high. Therefore, to protect people and electrical equipment contained in cabinets, medium voltage cabinets have strict requirements on construction and installation standards.


Nội dung được phát triển bởi đội ngũ truongchuvananhue.edu.vn với mục đích chia sẻ và tăng trải nghiệm khách hàng. Mọi ý kiến đóng góp xin vui lòng liên hệ tổng đài chăm sóc: 1900 0000 hoặc email: hotro@truongchuvananhue.edu.vn